Useful EU, DIN, BS, AU/NZ, JIS,...... Steel DATA; Fabrication, Construction, Standard Comparison and more.......!!
 Units Conversion Table! Units Conversion Table!
 LINKS TO Pages: LINKS TO Pages:
- STEEL Grade Comparison between specifications ASTM-EN-BS-DIN-JIS-AS/NZ-GB STANDARDS
- API American Petroleum Institute Spec. for Line Pipe -1992
- API American Petroleum Institute Spec. for Line Pipe 42nd Edition-1st July 2000
- Structural Steel Specifications AS/NZS 3679.1 year 1996 including BHP-300 plus
- Structural Plates AS/NZS 3678, year 1996
- ASTM Standard for Structural Steels & Steel plates
- BS 4360 Weldable Structural Steels -Sections or Plates
- EN 10025, year 1993 Hot rolled products of Non-alloy structural steels
- EN 10025 - DIN 17100General Structural Steel
- AB year 1996 Hull- Ship Building Structural Steel plates up to 100 mm (4 in.)
- Loyd Register 1996 Hull Structural Steel plates
- GB700 year 1988 Standard of Carbon Structural Steel, Chaina,
- JIS G3302 Hot dip Zinc Coated Steel Sheets and Coils.
- JIS G3101 year 1995 Rolled steels for General Structure
- JIS G4051 year 1979, JIS G4103, 4105 Carbon and Alloy Steel (Cr, Mo, Ni, Ni-Mo Steel)
- JIS G4304 / G4305 year 1991 Hot Rolled /Cold Rolled Stainless steel plates, Sheets, Strips.. (JIS -ASME-DIN)
- JIS G4305, year 1991 Steel Surface Finishes Cold Rolled Stainless steel plates, Sheets, Strips
- Hardness Conversion Tables for steel
- BS 1387 year 1996 Standard -Welded Steel Pipes (ERW) light. medium, heavy ;
- JIS G3452 year 1997 (SGP) Carbon Steel pipes for ordinary Piping
- ASTM A106 ASTM A53 Carbon Steel API seamless or welded pipes
- ASTM A312 (ANSI B36.19,.....) Stainless Steel Pipes (Grades TP 304.... TP310)
- DIN 17175 Hot finished seamless Boiler Tubes and pipes
- JIS G3459 year 1997 Stainless steel pipes, dimensions and weights
- ASTM A285, A515, A516 Pressure Vessels Plates
- BS-EN 10028-2, year 1993 Steel Flat products for pressure purposes,
- BS-EN 10028-3, year 1993 Steel Flat products for pressure purposes,
- DIN17155 -EN 10083 Heat Resistant Plates
 Unified Numbering System of Ferrous Metals and Alloys Unified Numbering System of Ferrous Metals and Alloys
 European standards for metallic materials, EN Standards European standards for metallic materials, EN Standards
 US ASTM Standards List for Steel US ASTM Standards List for Steel
- Group of ASTM Standards for Steel Pipes, Tubes and Fittings
- Group of ASTM Standards for Steel Castings and Forgings
- Group of ASTM Standards for Steel Plate, Sheet, Strip and Wire |
 LINKS TO Pages: LINKS TO Pages:
Welding_of_Steel
- Welding of Steels,
- Welding Process
- The Welding Processes: Resistance Welding
- Welding Procedures and the Fundamentals of Welding
- Beam Welding and Thermit Welding
- Processes Related to Welding
- Classification and Designation of Welding Filler Materials
- Welding of Stainless Steels
- Welding Ultra-High-Strength Steels
- Welding For Repair and Surfacing
- Procedures for Repair Welding and Surfacing
- Surfacing for Wear Resistance: Part One
- Surfacing for Wear Resistance: Part Two
- Power Supply for Welding Processes
- Clad Metals
- Welding of Special Steels
- Welding of Tool Steels
- Welding Cast Iron and Other Irons
- Historical Development of Welding
- Welding of Reinforcing Bars
- Welding of Coated Steels
- Basic Principles of Arc Welding
- The Welding Industry and Its Future
 Steel specifications and applications Steel specifications and applications
- General Requirements for Rolled Steel for Structural Use
- Structural Steel for Ships
- Design for High-Temperature Applications: Part One
- Design for High-Temperature Applications: Part Two
- Austenitic and Ferritic Stainless Steels in Practical Applications: Part One
- Austenitic and Ferritic Stainless Steels in Practical Applications: Part Two
- Wear-Resistant Special Structural Steels
- Forging
- Application of New Hot-Rolled High-Strength Sheet Steels
- Austenitic Sandwich Materials
- Carbon and Alloy Steel for Mechanical Fasteners
- Steel Rolling
- Production of Sheet Bimetal
- The Rotary Forge
- Electromagnetic Sorting of Ferrous Metals
|
 Mild Steel & High Tensile Plates, Mild Steel & High Tensile Plates,
 Ship-Building Quality Plates, Ship-Building Quality Plates,
 Boiler-Pressure Vessels Plates. Boiler-Pressure Vessels Plates.
 Stainless Steel Plates Stainless Steel Plates
 Chequered Plates Chequered Plates
 Zinc-Coated Sheet Coils (JIS G3302) Zinc-Coated Sheet Coils (JIS G3302)
 Flat Bars, Round Bars, Square Bars, T Bars, Deformed Bars Flat Bars, Round Bars, Square Bars, T Bars, Deformed Bars
 Expanded Metals Expanded Metals
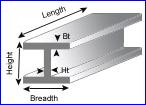 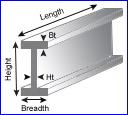
 Wide Flange Beams, Bearing Piles, IPN, I-Beam (JIS) Joists Wide Flange Beams, Bearing Piles, IPN, I-Beam (JIS) Joists
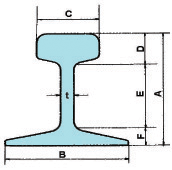
 Light Rails Crane Rails, European Profile, American British Standard 'A' Design, British Standard 'O', 'R' & 'N' U.I.C. and A.S.C.E.; A.R.E.A. Rails Light Rails Crane Rails, European Profile, American British Standard 'A' Design, British Standard 'O', 'R' & 'N' U.I.C. and A.S.C.E.; A.R.E.A. Rails |
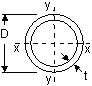 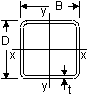
 Square (Cold Formed), Circular (Cold Formed) Square (Hot Finished), Square (Cold Formed), Circular (Cold Formed) Square (Hot Finished),
 Rectangular (Hot Finished), Circular (Hot Finished) Rectangular (Hot Finished), Circular (Hot Finished)
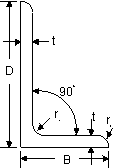 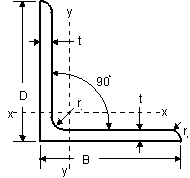
 Equal and Unequal Angles Equal and Unequal Angles
 US and Metric BEAM (s) size US and Metric BEAM (s) size
 ARBED "U" Section ARBED "U" Section
 U Shape JIS A5528 U Shape JIS A5528
|
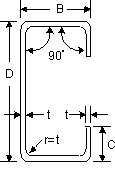 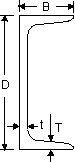
 Taper Flange Channel, Taper Flange Channel,
 Parallel Flange Channels, European Channels, Lipped Channels, Plain Channels Parallel Flange Channels, European Channels, Lipped Channels, Plain Channels
 Carbon and Alloy Steel (include hardness table) Carbon and Alloy Steel (include hardness table)
 GB700 -1988 China -Standard of Carbon Structural Steel GB700 -1988 China -Standard of Carbon Structural Steel
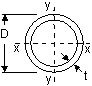
 Pipes (to BS 1387) Pipes (to JIS G3452) Pipes (to BS 1387) Pipes (to JIS G3452)
 Carbon Steel Line Pipe ; Stainless Steel Pipe (Seamless or Welded Carbon Steel Line Pipe ; Stainless Steel Pipe (Seamless or Welded
 Stainless Steel Pipe (JIS G3459 : 1997) Stainless Steel Pipe (JIS G3459 : 1997)
 Seamless Boiler Tubes & Pipes Seamless Boiler Tubes & Pipes
|
| |
 BASIC knowledge about World Steels Codes and Standards BASIC knowledge about World Steels Codes and Standards
European and Japanese Designation Systems:
Below some basics of European and Japanese designation systems are explained. Please refer to articles about corresponding national and international standards for more details.
DIN standards are developed by Deutsches Institut fur Normung in the Federal Republic of Germany. All West German steel specifications are preceded by the uppercase letters DIN followed an alphanumeric or numeric code. The latter method, known as the Werkstoff number, uses numbers only with a decimal point after the first digit.
JIS standards are developed by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee, which is part of the Ministry of International Trade and Industry in Tokyo. The JIS steel specifications begin with the uppercase letters JIS and are followed by an uppercase letter (G in the case of carbon and low-alloy steels) designating the division (product form) of the standard. This letter is followed by a series of numbers and letters that indicate the specific steel.
British standards (BS) are developed by the British Standards Institute in London, England. Similar to the JIS standards, each British designation includes a product form and an alloy code.
AFNOR standards are developed by the Association Francaise de Normalisation in Paris, France. The correct format for reporting AFNOR standards is as follows. An uppercase NF is placed to the left of the alphanumeric code. This code consists of an uppercase letter followed by a series of digits, which are subsequently followed by an alphanumeric sequence.
UNI standards are developed by the Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione in Milan, Italy. Italian standards are preceded by the uppercase letter UNI followed by a four-digit product form code subsequently followed by an alphanumeric alloy identification.
Swedish standards (SS) are prepared by the Swedish Standards Institution in Stockholm. Designations begin with the letters SS followed by the number 14 (all Swedish carbon and low-alloy steels are covered by SS14). What subsequently follows is a four digit numerical sequence similar to the German Werkstoff number.
|
|
|











